The Seattle Times recently focused on a long-simmering environmental concern unfolding in many states: aging underground storage tanks (USTs) (subscription may be required to preview the news article) on commercial properties. These USTs store gasoline and diesel fuel at gas stations across the Pacific Northwest and beyond. It’s not a question of ‘If’ but ‘When’ these tanks will leak.
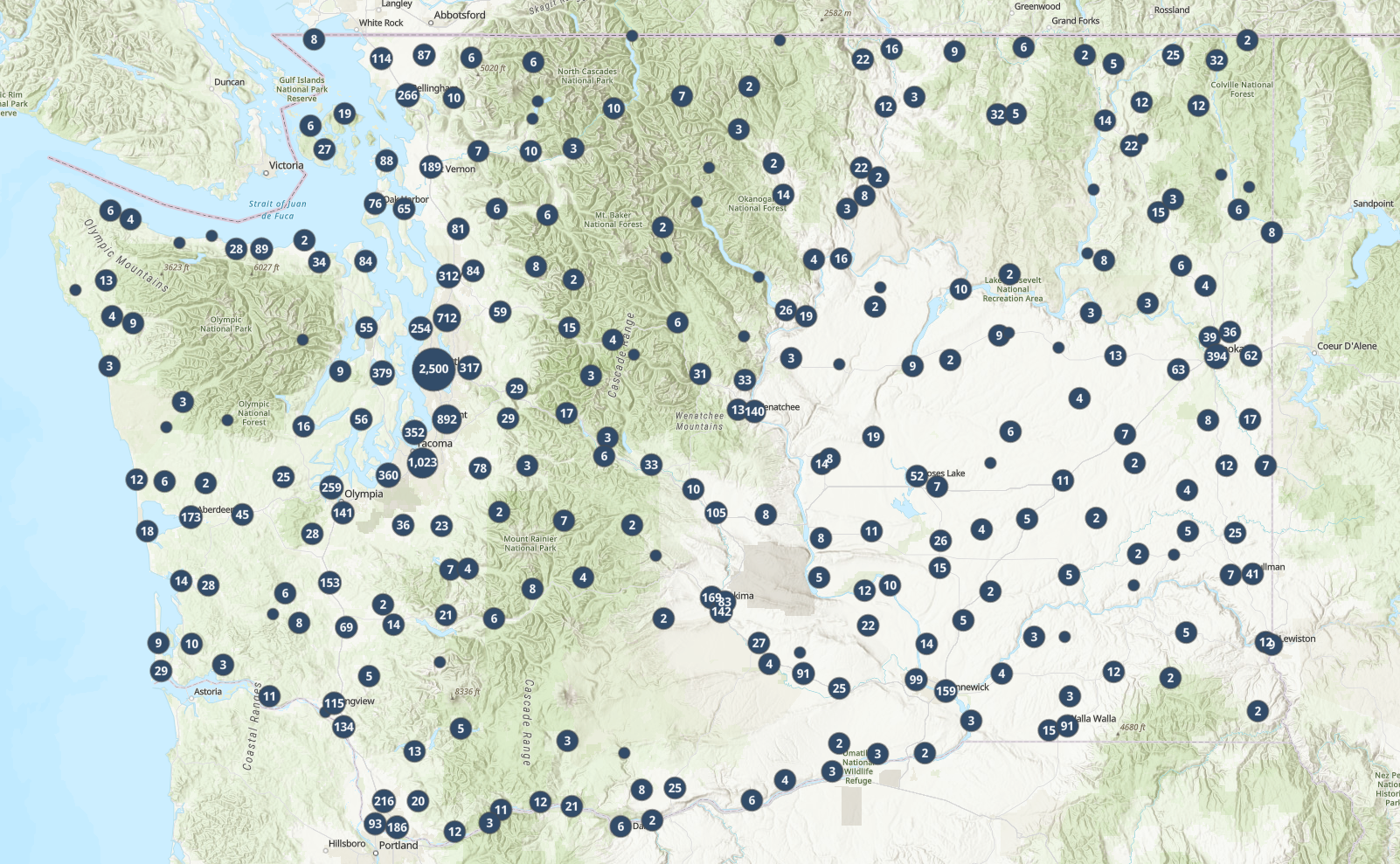
With nearly 2,500 known UST sites in need of cleanup in Washington, and over 7,500 USTs either beyond or rapidly approaching the end of their useful life, there is likely a UST site in your area. Here’s a map from the Washington State Department of Ecology for finding out what is in your neighborhood.
Where are the Contaminated Properties?
While leaking USTs can be a threat to the environment, the good news is that they often do not pose an acute health risk to people. Once a site has been properly investigated for environmental and human health risks, there are strategies that will manage the risk and cost of cleanup over time—particularly if the property is going to continue to be used for commercial purposes.
This corner store in Forks, WA recently had an old UST removed, fortunately only a small cleanup effort was needed
For small business owners – for example, the people running “Mom & Pop” gas stations — the cost alone of replacing aging USTs before they leak can be too much of a burden. And that is before the cost of a potential cleanup of any contaminated soil, which can balloon into a big financial liability.
Tools for Managing the Cost of Cleanup
In addition to the costs involved, the regulatory and cleanup process involved in addressing a leaking UST can feel overwhelming.
An environmentally impaired property does not have to be abandoned – there are paths to continuing business operations while successfully navigating the complexities of the cleanup. If you own a UST site, consider these initial steps for managing the cost of cleanup and avoiding a big financial burden all at once:
Complete a remedial investigation (RI) to define the extent of the contamination. If you don’t have insurance and you have questions about what this means for you financially, the Washington State Pollution Liability (PLIA) may be able to help through their revolving loan and grant program.
Evaluate the cleanup standards to see how to keep business going. If you are willing to accept certain restrictions on the property (e.g., no residential use), consider whether less stringent cleanup standards would still meet your business objectives while safely limiting risk to workers and customers.
Assess whether your site is eligible for the Washington State Department of Ecology’s Model Remedy process. This can streamline the cleanup selection process. If the USTs are still in the ground, removal of USTs and contamination to the extent practicable will still be required.
Talk to your environmental consultant about lower-cost options like environmental covenants for the property, engineering controls (like capping), and long-term monitored natural attenuation (MNA) of residual contamination. These strategies can be an effective way to reduce uncertainty around the future cost of managing the long-term environmental liability attached to a property and improve marketability.
Looking Towards Thriving vs. Blighted Properties
While these strategies do not always result in a “100 percent” clean bill of health for a property, they are proven and effective ways to add value back into environmentally impaired sites – both for the local community and the economy. A thriving corner store provides much more benefit to the community than a blighted, unused property where contamination remains in the ground anyway. There are better options for maintaining the productive use of the land while keeping people and the environment safe.
Contact Associate Engineer Eric Marhofer to learn more about UST site remediation and management strategies.